Healthy Blood Sugar Levels: Causes and Solutions
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, especially for those managing diabetes or prediabetes. This guide covers essential tips, information, and practical advice on how to keep your blood sugar within a healthy range. Consider adding a brief introduction that explains the importance of maintaining healthy blood sugar levels for overall health.
1. Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Understanding the normal range of blood sugar levels is key. Generally, a fasting blood sugar level between 70 to 99 mg/dL is considered healthy. Post-meal levels should remain under 140 mg/dL for non-diabetics.
2. Blood Sugar
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the body’s primary source of energy, sourced from the food we eat. It is vital to monitor blood sugar regularly, especially if you are at risk of diabetes or other related conditions. Use variations of the keyword, such as "glucose levels" and "blood glucose," to improve keyword diversity.
3. Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels fluctuate daily based on food intake, activity, stress, etc. Regular monitoring ensures you stay within a healthy range.
4. Blood Sugar Chart
A blood sugar chart can help you track your glucose levels. Here’s a simple breakdown:
| Blood Sugar Range | Condition |
|---|---|
| 70-99 mg/dL | Normal |
| 100-125 mg/dL | Prediabetes |
| 126+ mg/dL | Diabetes |
5. Normal Blood Sugar
Normal blood sugar levels can vary depending on the individual, time of day, and activity level. However, maintaining a fasting blood sugar level of 70-99 mg/dL is generally ideal.
6. High Blood Sugar
High blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia, occurs when glucose levels exceed the normal range. Symptoms include frequent urination, increased thirst, and fatigue. It’s important to address high blood sugar early to prevent complications.
7. Low Blood Sugar
Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, is when levels drop below 70 mg/dL. Symptoms include shakiness, confusion, dizziness, and in extreme cases, loss of consciousness.
8. What Level of Blood Sugar is Dangerous?
Blood sugar levels below 50 mg/dL or above 180 mg/dL can be dangerous and may require medical attention. Immediate action is needed to prevent serious health issues.
9. What Foods Lower Blood Sugar Immediately?
Some foods can help lower blood sugar quickly, such as:
- Leafy greens (e.g., spinach, kale)
- Whole grains (e.g., oats, quinoa)
- Foods rich in fiber (e.g., legumes, chia seeds)
- Cinnamon and turmeric (natural blood sugar stabilizers)
For a complete guide on managing blood sugar levels through diet and lifestyle, visit Easy Shop Store 24 today!

Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
The Blood Sugar Chart: A Comprehensive Guide
Here's a general overview:
- Fasting Blood Sugar:Normal: 70-99 mg/dLPrediabetes: 100-125 mg/dLDiabetes: 126 mg/dL and above
- Postprandial (after eating) Blood Sugar:Normal: Less than 140 mg/dLPrediabetes: 140-199 mg/dLDiabetes: 200 mg/dL and above
These ranges help individuals recognize whether their blood sugar levels fall within a healthy range or require intervention.
What Level of Blood Sugar is Dangerous?
Blood sugar levels can be perilous when they are excessively high or low. Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) both carry significant health risks.
- High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia): Levels above 180 mg/dL can lead to complications if sustained. Symptoms include frequent urination, increased thirst, and fatigue.
- Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia): Levels below 70 mg/dL are concerning and can cause dizziness, confusion, irritability, and fainting. Severe hypoglycemia can result in seizures or loss of consciousness.
Dr. Oz Blood Sugar Insights for Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
suggests:
- Balanced Diet: Incorporate fiber-rich foods such as vegetables, whole grains, and legumes to stabilize blood sugar.
- Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises can be beneficial.
Glucose Levels: Understanding and Managing Your Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Glucose is commonly known as blood sugar. It is the main type of sugar in the blood. It is also the body’s primary source of energy. Managing your glucose levels is essential for maintaining overall health, especially for those at risk of or living with diabetes. Here's a detailed breakdown of glucose levels, how to monitor them, and tips for keeping them within a healthy range.
What are Glucose Levels?
Glucose levels refer to the amount of sugar present in your bloodstream. Your body derives glucose from the food you eat, especially carbohydrates. It uses insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, to help cells absorb glucose and convert it into energy.
Normal Glucose Levels/ Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
For most individuals, normal glucose levels fall within a specific range:
- Fasting glucose levels (before eating): 70-99 mg/dL
- Postprandial glucose levels (after eating): Under 140 mg/dL for non-diabetics
Keeping glucose within these ranges is important for maintaining steady energy and preventing complications like diabetes or hypoglycemia.
High Glucose Levels (Hyperglycemia)
When glucose levels rise above the normal range, it is called hyperglycemia. Common causes include:
- Overeating, especially carbohydrate-heavy meals
- Lack of physical activity
- Stress or illness
- Insufficient insulin in the body
Symptoms of high glucose levels:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Headaches
Low Glucose Levels (Hypoglycemia)
Low glucose levels, or hypoglycemia, occur when blood sugar drops below 70 mg/dL. This can happen if you skip meals, over-exercise, or take too much insulin. Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Symptoms of low glucose levels:
- Shakiness
- Sweating
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Confusion
- Anxiety or irritability
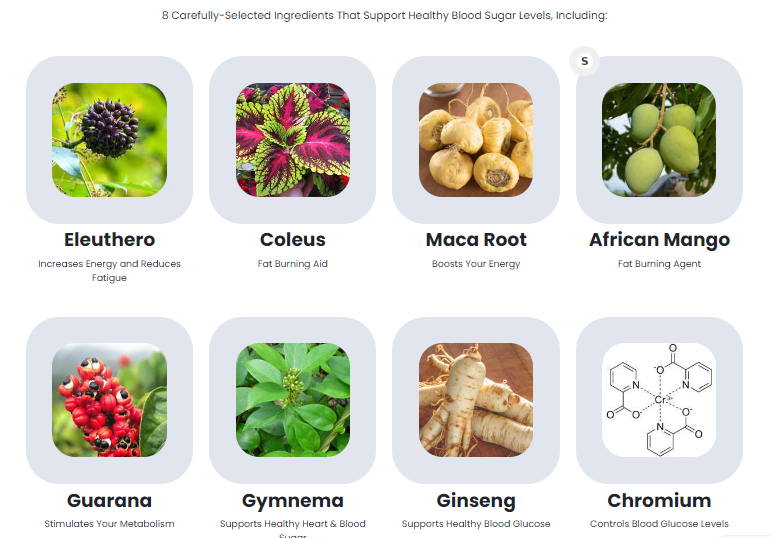
Dietary Supplements for Blood Sugar Management
Certain supplements have shown promise in supporting healthy blood sugar levels:
- Chromium: This trace mineral enhances insulin action and can improve glucose metabolism.
- Cinnamon: Some studies suggest cinnamon may lower blood sugar by increasing insulin sensitivity.
Low Blood Sugar Management
For those experiencing hypoglycemia, quickly consuming fast-acting carbohydrates can help. Examples include glucose tablets or juice. This can quickly raise blood sugar levels to a safer range.
Long-term Strategies for Healthy Blood Sugar Levels Management
Consistent Monitoring- Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is important. People can use devices such as glucometers or continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) to track it. This practice helps individuals understand the effects of different foods, activities, and stressors on their blood sugar.
Nutritional Considerations-Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Adopting a diet that emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods can be beneficial. This includes:
- Low Glycemic Index Foods: Foods that cause a gradual rise in blood sugar, such as oats and legumes, are preferable.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporating sources of omega-3 fatty acids, like fish and flaxseeds, can support metabolic health.
Lifestyle and Behavioral Changes
- Conclusion
Effective blood sugar management requires a multifaceted approach, combining lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and, when appropriate, the use of supplements.

Discover more from Easy Shop Store 24
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
